In our last blog on the topic of corrosion, we discussed how corrosion control can be a “headache”, and how controlling corrosion implies controlling the man-made contributors such as corrosion fatigue, which is a very dominant corrosion factor. Nowadays, integrated computational material engineering (ICME) and recent advances in computational capabilities can alleviate that “headache”. VPS-MICRO® is a probabilistic ICME tool that deals with fatigue problems. It builds a Virtual Twin® of the microstructures of any existent component, product or a fleet of products.
VPS-MICRO is a multiscale tool that can receive data from continuum simulations, such as nodal or element solutions from Finite Element Analysis (FEA), and extends the simulation to the microstructural level. One can now accurately consider the microstructural complexities that make geometrically-identical test specimens have significantly different fatigue lives, even in well-controlled laboratory tests. The fatigue life variation caused by the microstructure is compounded by other variations in actual products in the field. VPS-MICRO overlays complex microstructures (with probabilistically-generated material properties) onto the continuum solutions, and runs simulations by transitioning cracks from nucleation to crack growth to final failure. Monte Carlo formulae are used to generate the complex microstructure: grain sizes, defects, orientations, frictional strengths, etc. The theory of VPS-MICRO is based on cyclic crystal plasticity, microstructural small flaw fracture mechanics, and long crack linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM). The main output result from VPS-MICRO is the probability of failure of the tested component. It also provides more detailed information about the failed components, such as the expected statistical distributions of lives (in cycles), micro-cracks and the features on the fracture surface (i.e. grain sizes and orientations, frictional strengths and micro-stresses). All of these outputs can be visualized by using VPS-MICRO’s post-processor.
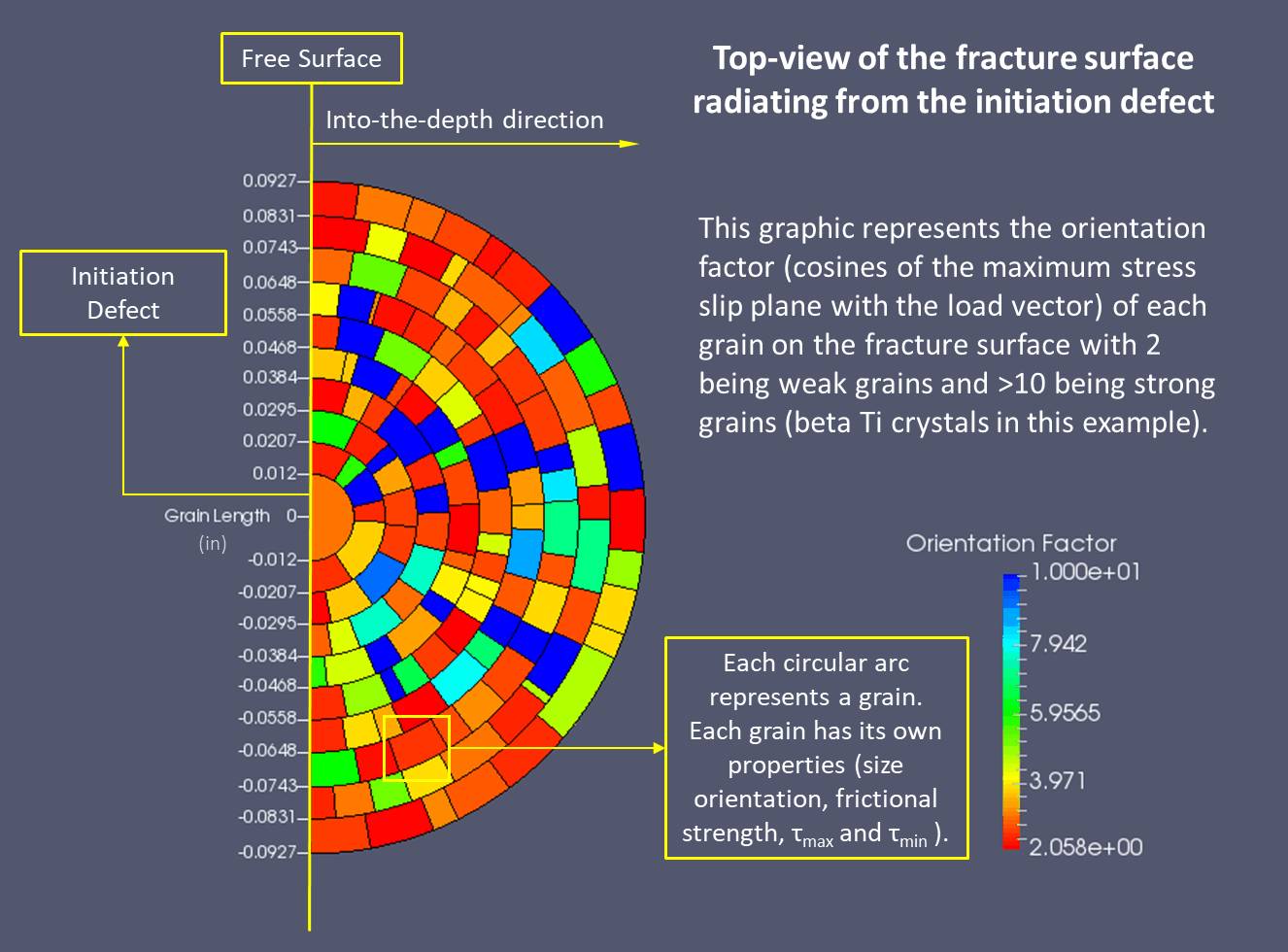
In VPS-MICRO, corrosion is considered one of the microstructural complexities. Corrosion results in geometrical microfeatures on the corroded surface. These microfeatures induce high stress concentrations (kt) that initiate cracks more easily than a smooth surface. As an example, corrosion features in aluminum occur as big pits (macro-pits) that encompass smaller pits (micro-pits). These pits result in high stress concentration gradients that die out over a very thin layer into the depth. Stress gradients caused by micro-pits are called micro-gradients, while stress gradients caused by macro-pits are called macro-gradients. Micro-gradients can have a higher stress concentration than macro-gradients, due to the extremely rough topology on the microstructural scale, but they also die out faster.
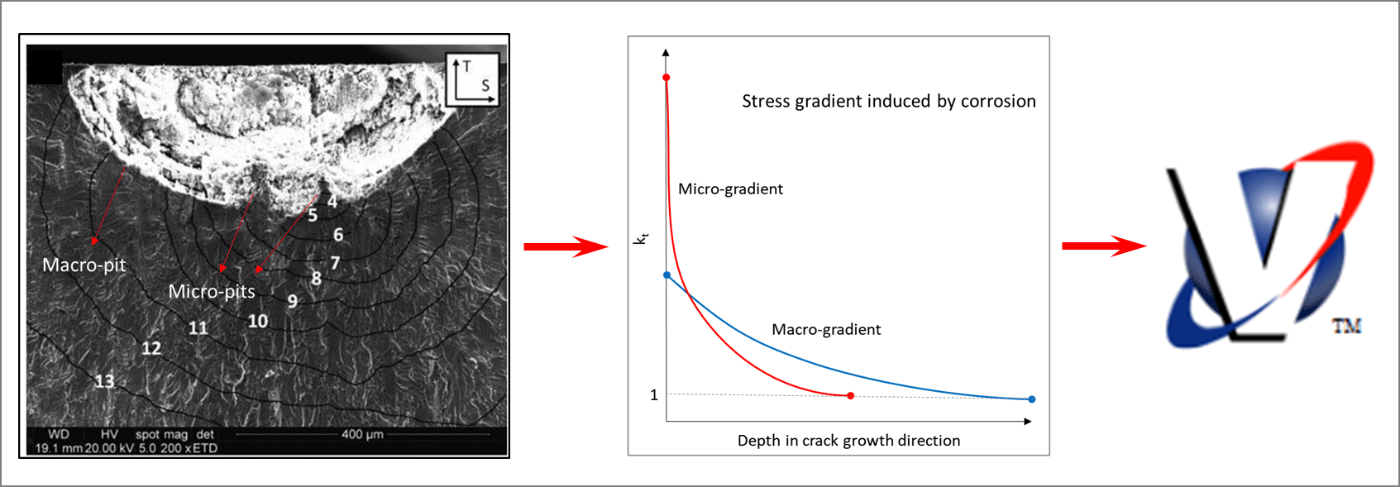
Although the high stress occurs over a very small surface layer, corroded surfaces can reduce fatigue life by several orders of magnitude. This kt occurs over a small scale, where the variation in the material’s microstructure greatly influences nonhomogeneous properties. In VPS-MICRO, these stress concentrations are applied concurrently to the crack growth models (nucleation, short crack, and long crack) as the crack grows. Microstructural small flaw fracture mechanics (SFFM) must be used to properly account for the thin layer of roughened surface. Continuum analysis methods do not work at this scale. To learn more about the theory behind stress and crack propagation adopted in VPS-MICRO, check out this example.
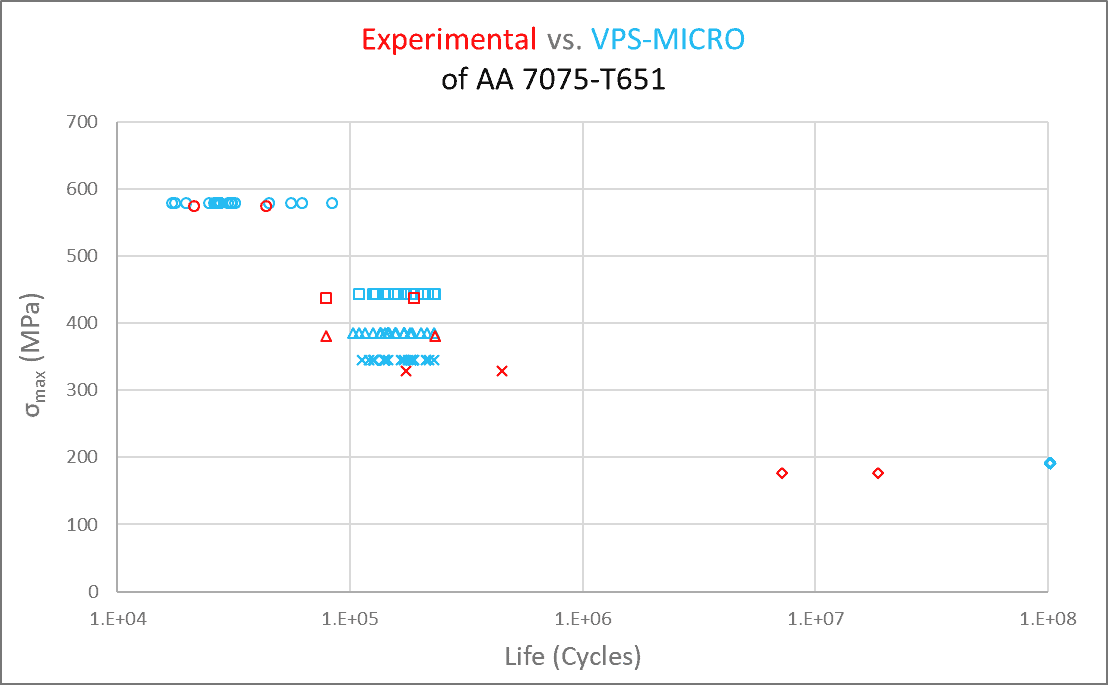
From previous projects, VPS-MICRO has provided reliable predictions of the lives of corroded components. The predicted results were within acceptable bounds of the experimental results, which highlights the benefits of using VPS-MICRO to build Virtual Twins of potentially corroded components. Employing this technology reduces the number of empirical physical tests required to qualify a component. VPS-MICRO provides time- and cost-effictive assessments of materials and designs. This decreases lead time, increases return on investment (RoI), and most definitely cures the corrosion control headache!



Leave A Comment